- Artificial Intelligence
- Data
- Data Science
- Features
- Generative AI
- Machine Learning
-
Modeling
- Autopilot Mode
- Classification
- Confusion Matrix
- Cross-Validation
- Deep Learning Algorithms
- Machine Learning Model
- Machine Learning Model Accuracy
- Machine Learning Model Deployment
- Model Blueprint
- Model Fitting
- Model Interpretability
- Model Tuning
- Multiclass Classification
- Neural Network
- Open Source Model Infrastructure
- Overfitting
- Regression
- Training Sets, Validation Sets, and Holdout Sets
- Underfitting
- Predictions
- View global site search results
- A
- AI Engineer
- AI Observability
- AIOps
- Artificial Intelligence Wiki
- Automated Machine Learning
- Autopilot Mode
- B
- Big Data
- C
- Citizen Data Scientist
- Classification
- Cognitive Computing
- Confusion Matrix
- Cross-Validation
- D
- Data Collection
- Data Governance
- Data Insights
- Data Management
- Data Preparation
- Data Profiling
- Data Science
- Deep Learning Algorithms
- E
- Explainable AI
- F
- Feature Engineering
- Feature Impact
- Feature Selection
- Feature Variables
- G
- Generative AI
- L
- Large Language Model Operations (LLMOps)
- M
- Machine Learning
- Machine Learning Algorithms
- Machine Learning Life Cycle
- Machine Learning Model
- Machine Learning Model Accuracy
- Machine Learning Model Deployment
- Machine Learning Operations (MLOps)
- Model Blueprint
- Model Fitting
- Model Interpretability
- Model Monitoring
- Model Tuning
- Multiclass Classification
- N
- Natural Language Processing
- Neural Network
- O
- Open Source Model Infrastructure
- Overfitting
- P
- Prediction
- Prediction Explanations
- Predictive Maintenance
- Production Model Governance
- Production Model Lifecycle Management
- R
- Regression
- S
- Scoring Data
- Semi-Supervised Machine Learning
- Stacked Predictions
- Supervised Machine Learning
- T
- Target Leakage
- Target Variable
- Text Mining
- Training Sets, Validation Sets, and Holdout Sets
- U
- Underfitting
- Unsupervised Machine Learning
- W
- What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- View global site search results
- Artificial Intelligence
- Data
- Data Science
- Features
- Generative AI
- Machine Learning
-
Modeling
- Autopilot Mode
- Classification
- Confusion Matrix
- Cross-Validation
- Deep Learning Algorithms
- Machine Learning Model
- Machine Learning Model Accuracy
- Machine Learning Model Deployment
- Model Blueprint
- Model Fitting
- Model Interpretability
- Model Tuning
- Multiclass Classification
- Neural Network
- Open Source Model Infrastructure
- Overfitting
- Regression
- Training Sets, Validation Sets, and Holdout Sets
- Underfitting
- Predictions
Multiclass Classification
What does Multiclass Classification Mean?
There are two types of classification algorithms: binary and multiclass. In multiclass classification, each record belongs to one of three or more classes, and the algorithm’s goal is to construct a function which, given a new data point, will correctly identify the class into which the new data point falls.
For example, a multiclass algorithm can determine which parental guideline rating a movie is likely to receive – “PG,” “TV-14,” “R,” “G,” etc. – based on patterns it learns from this sample movie dataset:
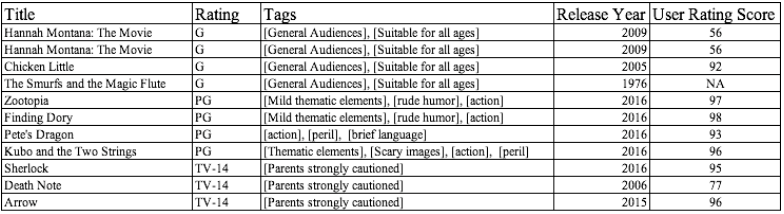
The movies have also been tagged with descriptions – “General Audience,” “Suitable for all ages,” etc. This is different than the rating system in that each movie can be described by one or more of the tag categories, which is known as a multi-label classification problem.
Why is Multiclass Classification Important?
Multiclass classification extends the number of practical business problems into which analysts can gain insight with machine learning. For example, it enables a business to predict which product a customer will purchase next from several options, allowing the business to estimate expected revenue and adjust business practices and resources accordingly.
DataRobot + Multiclass
The DataRobot AI platform automatically defaults to the appropriate classification technique for your target variable and runs a wide array of classification algorithms on your data. Then, the feature impact functionality will expose which inputs are the most important for determining classes, and the confusion matrix will show how accurate each algorithm is for your dataset.




