Citizen Data Scientist
What does Citizen Data Scientist Mean?
“Citizen Data Scientist,” a term coined by Gartner, refers to an advanced data analytics professional or data professional who needs or wants to implement machine learning technology. Organizations of all sizes across industries strive to be more data-driven, but with a worldwide shortage of trained data scientists, businesses are empowering their data analytics professionals and other domain information experts with the tools and support they need to become citizen data scientists. The term itself tends to be used more as a label – it’s unlikely that someone would use it to refer to themselves.
Citizen data scientists typically reside in a line of business such as sales, marketing, finance, or human resources, and possess a deep domain knowledge of the business challenges their department faces. Armed with powerful software, they perform detailed diagnostic analysis and create machine learning models to supplement the work that previously required a data scientist, statistician, or mathematician.
Citizen data scientists work in tandem with data scientists in most artificial intelligence (AI)-driven organizations on projects that require detailed business expertise. This allows traditionally educated data scientists to focus on more complex projects that impact the entire organization rather than the KPIs of one specific department.
Why are Citizen Data Scientists Important?
Data analytics professionals typically focus on finding trends in data from events that have already happened (descriptive analytics) and express their results in dashboards, static reports, and graphs. Now, however, citizen data scientists, software engineers, data engineers, and AI engineers have powerful tools enabling them to solve business problems using data with greater depth and breadth than their data analytics professional peers. They can build models to recommend a next best course of action, to identify prospects most likely to buy a product, to determine which loans are most likely to default, and more. Their influence is so significant that Gartner predicts that the amount of advanced analysis and business value produced by citizen data scientists will surpass that of data scientists as soon as 2019.
DataRobot + Citizen Data Scientists
Data analytics professionals possess the deep domain expertise to recognize the core business challenges of their department and a thorough understanding of the available data but often lack the ability to perform some of the data science tasks that distinguish an analyst from a citizen data scientist. The DataRobot AI Platform replicates the tasks and processes that up to now have been manually performed by data science Ph.D.s, allowing users to implement machine learning solutions without writing code or preselecting algorithms.
Citizen data scientists can upload a dataset to DataRobot and pick a target variable based on the practical business problem they wish to solve. The platform automatically applies best practices for data preparation and preprocessing, feature engineering, and model training and validation. DataRobot selects the most appropriate algorithms for the data and target variable and ranks trained models according to their accuracy so that citizen data scientists can easily interpret and select the most appropriate model for the business problem. DataRobot automatically uncovers insights that users might not have noticed and keeps guardrails in place so that users can trust the output of their models.
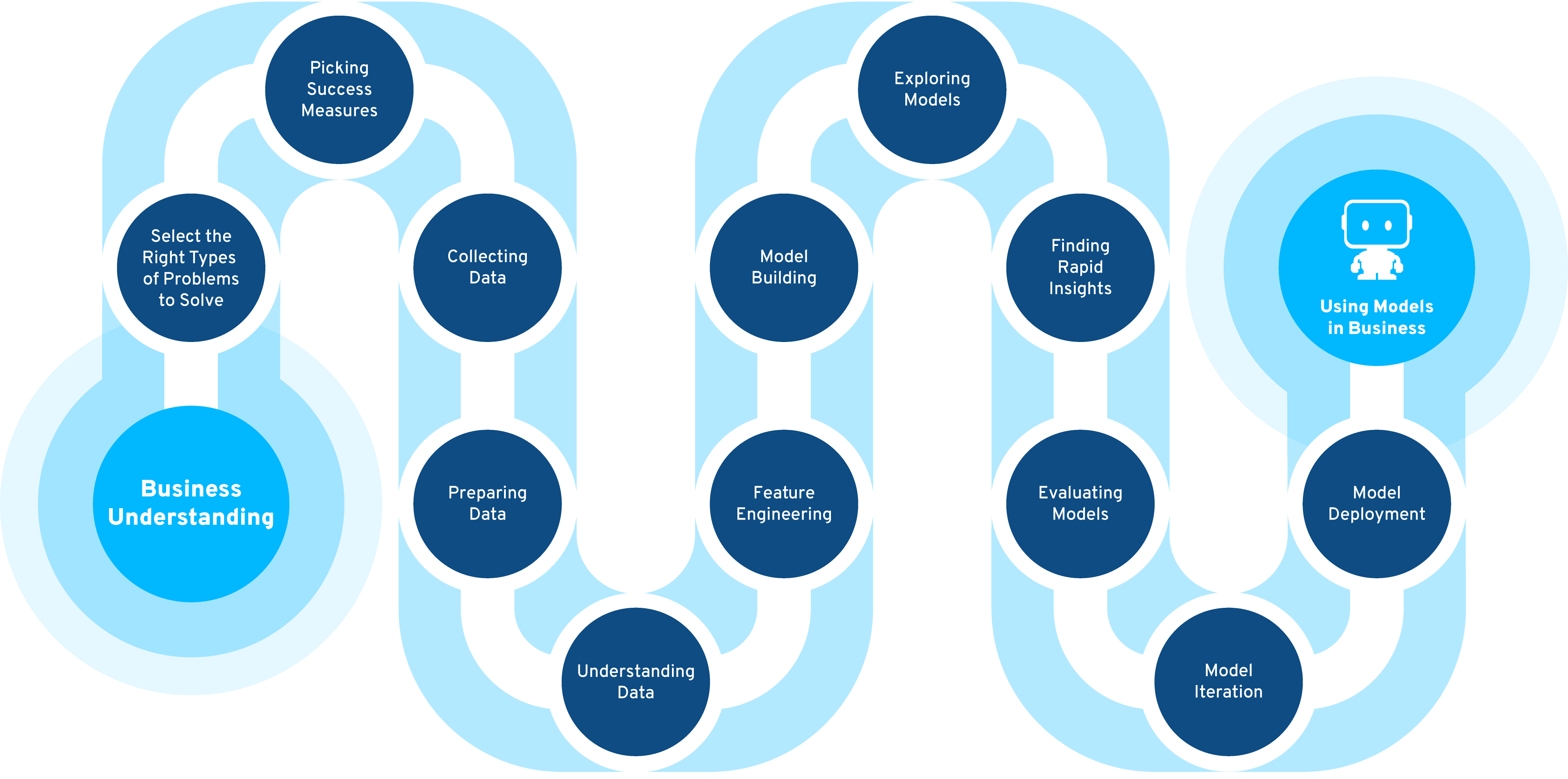
Data Analytics Professional to Citizen Data Scientist Learning Path
Gartner estimates that more than 40% of data science tasks will be automated by 2020, resulting in greater productivity and broader usage of data and analytics by citizen data scientists, software engineers, data engineers, and AI engineers, and an increase in the analytic maturity of the organization as a whole.




